Innovative Intersections
Also known as Restricted Crossing U-Turn

Source: Google Earth. Bandera Road at FM 1560, San Antonio, TX. RCUT with offset side roads.
What is an RCUT?
A Reduced Conflict U-turn (RCUT) intersection, also called a Restricted Crossing U-Turn, is an innovative traffic design that redirects minor road left-turn and through movements to a downstream U-turn. This design reduces conflict points, improving safety and operational efficiency.
RCUT intersections may be signalized or unsignalized depending on traffic volumes and site context.
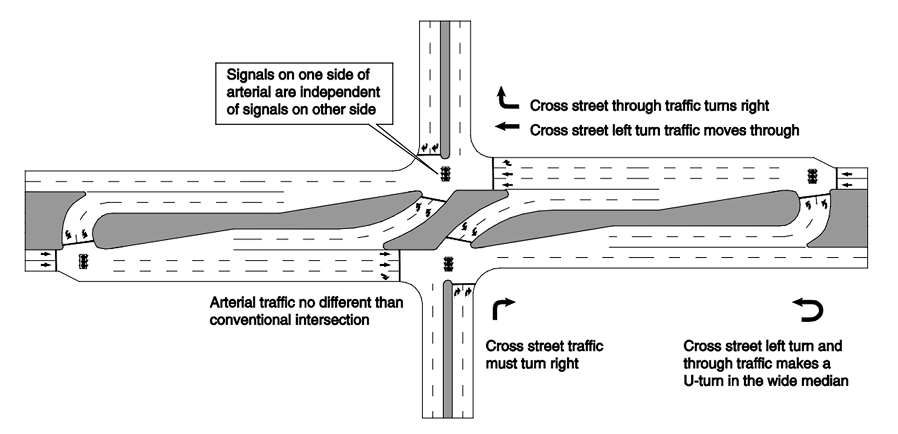
Source: TxDOT Roadway Design Manual
The following design principles characterize RCUTs:
- Major road through, right, and left turn movements remain unchanged.
- Minor road maintains right turn movements. Through and left turn movements are redirected to right turn with a downstream U-turn crossover.
RCUTs are a flexible intersection treatment with common characteristics shared across all sites. Some RCUTs may have additional site-specific features.
- Common to all RCUTs: Main road makes all movements at intersection with minor road. Minor road makes right turns only.
- Common to all RCUTs: Downstream U-turn movements at median crossovers for minor road left and through movements.
- Site dependent: Other U-turn lanes and wide medians are designed for large trucks and trailers.
- Site dependent: Signalized or unsignalized
- Site dependent: Pedestrian facilities

What are the benefits of RCUTs?
Enhanced safety
- RCUT intersections reduce fatalities and injuries by 63 percent.
- RCUT intersections reduce crossing-type conflict points from 16 at a conventional intersection to 2, eliminating many severe crash opportunities.
Sources: FHWA (above), FHWA (below)

RCUT intersections improve traffic flow by rerdirecting left-turn and thru movements from minor roads. Instead of crossing busy highways, drivers turn right onto the main road and then make a U-turn at a downstream location.
Reconfiguring an intersection into an RCUT can increase intersection throughput by up to 30 percent and reduce delay by as much as 40 percent.
Source: FHWA



