Cybersecurity
Report cybersecurity issues
Have you been a victim of a phishing attack, a spoofing email, or an attempt to mislead you by someone impersonating an employee of TxDOT? There are persistent cybersecurity threats to business and individuals. It is important that TxDOT partners and the public remain vigilant in keeping threats at bay. As cybersecurity criminals become more sophisticated in their methods, it is important that you do your part in understanding and identifying threats and being secure.
Protect yourself by being on the lookout for the most current cybersecurity threats identified in the Alerts section below, and report any suspected emails or other cybersecurity threats using the Cybersecurity Incident Form below. To learn more about the different trends within cybersecurity, like email phishing, review the FAQ’s below, and visit our Resources page for pertinent cybersecurity documentation.
Alerts
Reported phishing attacks targeting TxDOT staff, vendors, and trusted business partners have significantly increased in recent months.
While the threat of phishing and social engineering always requires vigilance and careful evaluation, understanding individual trends within phishing is vital to identifying and circumventing related threats. One such trend, sometimes known as “spoofing” or email impersonation, is actively on the rise.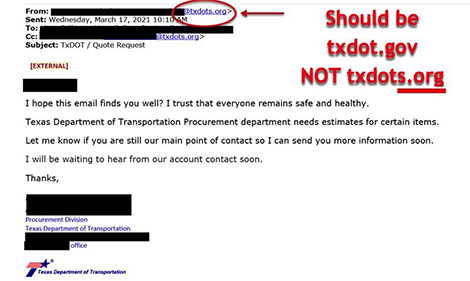
Spoofing is the act of impersonating or disguising an email communication from an unknown source as being from a known, trusted source.
Cybercriminals are sending spoofed (impersonated) emails — appearing to be from a TxDOT office — inviting recipients to fulfill a certain task included with the spoofed emails. These emails are not from TxDOT.
How can you evaluate a sender?
The display name of a sender can easily be manipulated to show any text. However, by fully reviewing the sender’s email address, you can identify mismatched or inaccurate details and domains.
TxDOT emails will always end with @txdot.gov. Please report any related examples of TxDOT spoofed emails via the Cybersecurity Incident Form below.
We have received your water draining report located near 200 East 11th Street in Austin, TX. We will respond to your submission in 4-10 days.
FAQs
Spoofing is the act of impersonating or disguising an email communication from an unknown source as being from a known, trusted source. The goal of email spoofing is to get the recipients to open and even respond to the request.
How can you evaluate a sender?
The display name of a sender can easily be manipulated to show any text. However, by fully reviewing the sender’s email address, you can identify mismatched or inaccurate details and domains.
TxDOT emails will always end with txdot.gov. Be on the look out for those that have been altered in anyway.
If you receive a spoofing email:
- Do not respond.
- Do not click on any links.
- Never give out personal information such as Social Security numbers, mother's maiden names, passwords, or other identifying information in response.
- Use caution if you are being pressured for information immediately.
- If you get an inquiry from someone who says they represent TxDOT, call a phone number that has been verified on our website.
Please report any related examples of TxDOT spoofed emails via the Cybersecurity Incident Form below.
A phishing attack is the action or set of actions that the hacker takes in order to exploit the user. Poorly crafted emails for the classic email phishing scheme are often easy to spot due to poor grammar or misspelled words. The attackers are getting better and more technically sophisticated with the attacks that they launch. Though often simple messages, they can be very effective.
Phishing is primarily used in reference to generic email attacks where the attacker sends out emails to as many addresses as possible. The emails can state something about your account being compromised, so in order to catch as many people as possible they will use more commonly used services. The email will state something about your account having been compromised and that you need to click on this link and verify that everything is ok, or not. The link will usually do one of two things, or both:
- Take the user to a malicious website that looks a lot like the real site, e.g. www.TxDOTS.gov vs the real www.TxDOT.gov. Note the extra ‘s’ on the first URL.
- Infect the user’s computer with downloaded malware. If malicious software is installed onto their computer it could be used for a future attack. The malware could be anything from a keystroke logger, to capture their logins or their credit card numbers, to ransomware that will encrypt their drive contents and not release it until money is paid, usually in the form of bitcoins.
How do you identify other signs of phishing?
You can refresh your memory of what to look out for with the tips below. Remember that it is better to be safe than sorry.
- Threats, urgent calls to action or the promise of an action which is “too good to be true.”
- Use of poor language, grammar, punctuation, or a different format than accustomed.
- Unexpected and suspicious links and attachments.
- Requests for financial, proprietary, or personal information that normally would not be requested via email or through the respective channels.
When in doubt, make sure to validate the legitimacy of an email by contacting the sender (if trusted) or another trusted source before sending a reply or opening any attachments.
What is Social Engineering?
Social engineers use manipulation to trick and deceive you into unintentionally providing information and access to places, data, or systems. They may use email, as in phishing attacks, or a variety of other means including requests made in person, over social media, on voice calls (AKA vishing) and SMS text messages (AKA SMiShing).
Social engineering scams rely on human interaction, communication, and a sense of urgency to convince you to trust the exchange. They use techniques that exploit an established relationship, include a sense of urgency, and, or a form of heightened emotion.
To overcome social engineering threats, remember to always validate requests prior to responding, confirm identity whenever possible, be careful of opening unsolicited emails, links, or attachments, never share sensitive information, and always report suspicious activity.
To make a report, please contact us through the Cybersecurity Incident Form.
- Select the type of attack you experienced (phishing, spoofing, or do not know).
- Describe the attack.
- List your contact information so we can reach out to you if necessary.
