4.7.9 Sight Distance on Horizontal Curves
Where an object off the pavement restricts sight distance, such as a bridge pier, bridge railing, median barrier, retaining wall, building, cut slope or natural growth,
the minimum radius of curvature is determined by the stopping sight distance.
The following equation applies only to circular curves longer than the stopping sight distance (S<L) for the pertinent design speed. For example, with a 50-mph design speed and a curve with a 1,150-ft radius, a clear sight area with a horizontal sight line offset (HSO) of approximately 20-ft is needed for stopping sight distance.
Where:
HSO =
horizontal sight line offset, ft S =
stopping sight distance (
), ft R =
radius at centerline of inner most travel lane, ftThis method for calculating HSO is only exact when both the vehicle and sight obstruction are located within the horizontal curve. When the vehicle or sight obstruction are located outside of the horizontal curve (i.e., S>L) this method will result in an HSO slightly larger than required. In many instances the resulting additional clearance will not be significant. In some cases, the design should be checked either by using graphical procedures (2D or 3D) or computational methods to verify HSO. NHCRP 910 provides computational methods for verifying HSO.
In cases where complex geometries or discontinuous objects cause sight obstructions, graphical methods may be useful in determining available sight distance and associated offset requirements. Graphical methods may also be used when the circular curve is shorter than the stopping sight distance.
To check horizontal sight distance on the inside of a curve graphically, sight lines equal to the required sight distance on horizontal curves should be reviewed to ensure that obstructions such as buildings, hedges, barrier railing, and high ground do not restrict the sight distance required in either direction.
illustrates a graphical approach to determining horizontal sight distance in a curve.
Where sufficient stopping sight distance is not available because a railing, longitudinal barrier or other features constitutes a sight obstruction, alternative designs should be considered. Potential alternatives include:
- Increasing the offset to the obstruction; or
- Increasing the radius.
However, the alternative should not incorporate a shoulder width on the inside of the curve more than 12-ft because of the concern that drivers will use wider shoulders as a passing or travel lane.
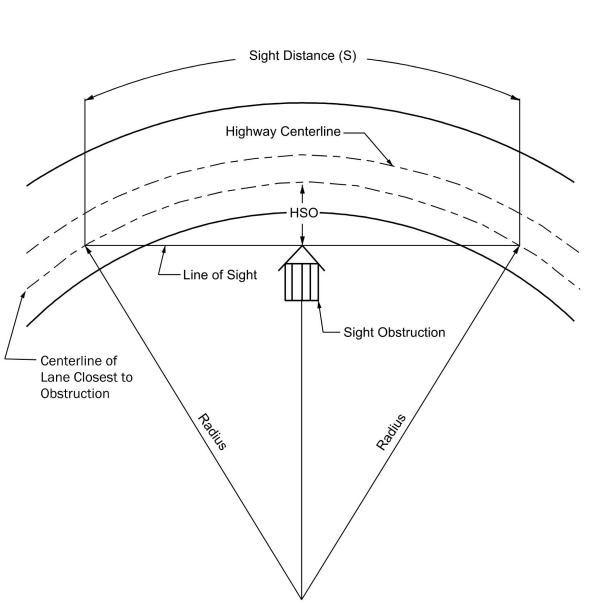
Figure 4-3: Diagram Illustrating Components for Determining Horizontal Sight Distance
Source: AASHTO A Policy on Geometric Design of Highways and Streets