18.4.3 Buffered Bike Lanes
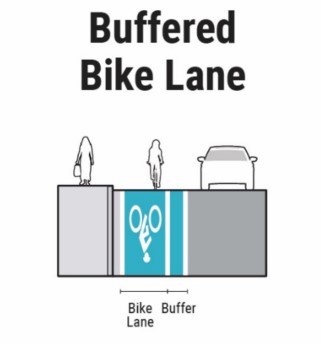
Figure 18-20: Example Buffered Bike Lane Schematic
A buffered bike lane is a one-way bike lane that is separated from the adjacent motor vehicle lane or parking lane by a striped buffer area that may include chevrons, diagonal lines, or wide pavement marking stripes. When sufficient roadway width is present, or if the number of travel lanes is reduced, a buffer may be striped between a bike lane and travel lane to provide additional comfort for both bicyclists and motorists. This provides space for bicyclists to pass one another or ride side by side without encroaching into a motor vehicle travel lane. The buffer adds to the perception of safety and encourages greater use of the on-street bicycle network. Providing added separation between motorists and bicyclists who may be traveling at substantially different speeds appeals to a wider array of bikeway users.
18.4.3.1 Application
See
in
for initial recommendations on when to use a buffered bike lane. The criteria below defines the criteria for all available applications for all speeds.
18.4.3.2 Bike Lane Width
The desirable useable width of a buffered bike lane is 5 to 7-ft exclusive of the buffer. The minimum useable width is 4-ft exclusive of the buffer. The usable width of the bike lane is measured from the outside buffer stripe to either the gutter joint or 1-ft from the nominal face of a monolithic curb.
18.4.3.3 Buffer Width and Considerations
Buffers should be a minimum of 2-ft wide for speeds of 45 mph or less, and 3-ft wide for 50 mph or greater.
Buffers generally consist of a combination of standard longitudinal markings and crosshatching. Diagonal or chevron crosshatch markings are optional; however, they are recommended in locations with buffers that exceed 2-ft in width.
Where provided, crosshatching should be provided at a regular interval. Typical spacing is 20-ft with some locations reduces to as low as 5-ft where engineering judgement determines a more frequent spacing is desirable. See
for examples of bike buffer lane types.
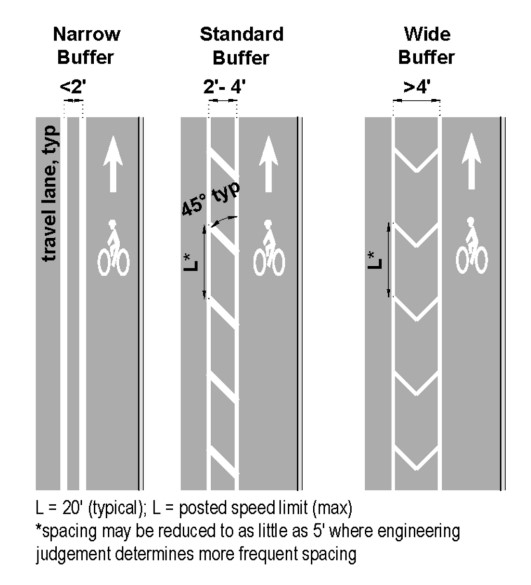
Figure 18-21: Examples of Buffered Bike Lane Types
18.4.3.4 Signing and Marking
The stripe near the travel lane should be 6-in wide, while the stripe near the bicycle lane can be four inches. If buffer is 3-ft wide, diagonal hatching should also be marked. If buffer is wider than 3-ft, chevron hatching should also be marked.
Buffers can be striped between travel lanes and bike lanes, between bike lanes and parking lanes, or both.
Bicycle markings and signage should be used and are the same as a conventional bike lane.
18.4.3.5 Bicycle Design Speed
Not applicable as the roadway will be designed to accommodate motorist target design speeds which will exceed bicyclist’s design speed.
18.4.3.6 Cross Slope and Grade
Not applicable.
18.4.3.7 Other Considerations
Not applicable.