8.1 Introduction
8.1.1 Overview
An alternatives analysis is a decision-making process where multiple alternatives are evaluated and a preferred alternative selected. This chapter describes three important aspects of the alternatives analysis process (criteria definition, alternative development, and alternative evaluation), and provides a sample report outline. General characteristics of an alternatives analysis, as well as general steps, are provided below.
Alternatives analyses includes:
- Defining evaluation criteria, such as safety, mobility, and environmental performance measures;
- Developing project alternatives, defining evaluation criteria, and selecting a preferred alternative through a detailed screening process; and
- Evaluating, comparing, and prioritizing alternatives based on evaluation criteria
The alternatives analysis process involves the following steps. This is represented in the flow diagram in .
- Determine purpose and need
- Set goals and objectives
- Define overall project scope and study area
- Define evaluation criteria
- Establish performance measures
- Develop alternatives a. Refine project scope, study area, and performance measures as needed
- Evaluate alternatives
- Score, rank and select preferred alternative
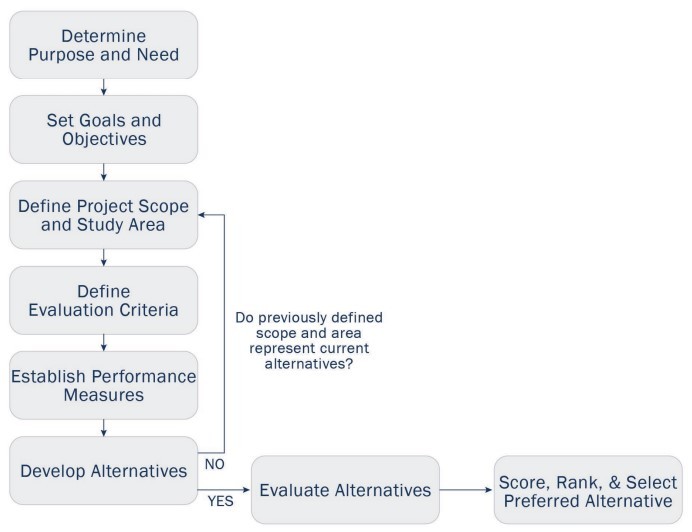
Figure 8-1: Alternatives Analysis Process
8.1.2 Purpose and Intended Use
The purpose of this chapter is to provide a general guidance to conduct alternatives analysis. It includes procedures to screen and evaluate alternatives in terms of traffic and safety analysis, such as reduction in delay or travel time and reduction in crash severity and frequency. This chapter is intended to be used as a resource and informational guide for alternative development, criteria definition, and presentation of alternatives analysis results (alternative evaluation). Procedures for conducting traffic analyses, necessary to evaluate alternatives, are detailed in
Chapters 4, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13,
and 14
. This chapter emphasizes developing alternatives and evaluating alternatives.8.1.3 Limitations
This chapter does not cover all aspects of alternatives analysis; it is limited to the traffic and safety aspects of alternatives analysis. If National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) is pertinent or will be pertinent, such as in the creation of an Environmental Impact Statement (EIS) or an EA, the NEPA guidance for alternatives analysis needs to be followed. Most projects are deemed Categorical Exclusion (CE) and do not involve the NEPA process.