Section 6: Glossary of Terms and Formulas
Introduction
The following terms and formulas appear in this manual and
in discussions of highway lighting. For electrical terms not listed
here, consult the National Electrical Code (NEC).
AASHTO
American Association of State Highway Transportation Officials
Alternating Current (AC)
Current and voltage alternates from maximum positive to maximum
negative in a sinusoidal pattern.
Ampere (A)
The unit of electric current.
Ballast
A device that includes a transformer that modifies incoming
voltage and current to provide the circuit conditions necessary
to operate electric discharge lamps.
Blanket Agreement
An agreement covering installation, operation, and maintenance
responsibilities between a municipality and the Texas Department
of Transportation (TxDOT) for all safety or continuous lighting within
the municipality.
Breakaway Support
A light pole support designed to shear easily under vehicular
impact. The breakaway feature can be an aluminum transformer base,
a frangible insert between pole base foundation, a slip base, or
other device. The breakaway support must meet current AASHTO and
FHWA requirements.
Candela or Candlepower (cd)
The unit of luminous intensity emitted by a light source in
a given direction.
Capacitance (C)
Ability to store energy in an electrostatic field. Measured
in farads or microfarads.
Clear Zone
The area provided along highways to allow vehicles veering off the travel lane an opportunity for safe recovery or stopping. The clear zone width is always measured from the edge of the travel lane and depends on several roadway factors. The contains a full discussion of the clear zone ("Horizontal Clearance to Obstructions") and provides the minimum and desirable widths for various roadways.
Complete Interchange Lighting
The lighting, within the limits of the interchange, of the
main lanes, direct connections, ramp terminals, and frontage road-crossroad
intersections. (See partial interchange lighting.)
Conductor
A flexible wire that may be stranded or solid, insulated or
bare, and that can carry electrical current.
Continuous Lighting
Roadway lighting providing uniform illumination on all main
lanes and direct connections and complete lighting for all interchanges.
Conventional Lighting
A highway lighting system in which the luminaires are typically
mounted no higher than 50 feet. (See also high mast lighting.)
Cutoff
A luminaire light distribution is designated as cutoff when
the candlepower per 1,000 lamp lumens does not numerically exceed
25 (2.5 percent) at an angle of 90 degrees above nadir (horizontal), and
100 (10 percent) at a vertical angle of 80 degrees above nadir.
Cutoff type luminaires usually have flat glass lenses. Cutoff ratings
have been replaced with BUG (Backlight, Uplight, Glare) ratings
by the IES.
Direct Current (DC)
Flow of electricity in a single direction.
Electrical Details (ED)
TxDOT's standard sheets showing specifications for electrical
specifications and standard construction practices for the installation
of conduit, conductors, ground boxes, electrical services, and other
electrical equipment.
Electrical Service
Point of receiving power from utility company. Typical service
voltages used on highway electrical systems are 120/240 VAC and,
240/480 VAC.
FHWA
Federal Highway Administration.
Floodlight
An aimable luminaire generally employed for spot or wide-angle
lighting.
Footcandle (FC)
English unit of measurement for the illumination (E) on a surface. (See "lux" for metric.) One footcandle is the illumination on a surface that is one foot from and perpendicular to a uniform point source of one candela. Combining the inverse square law and the cosine law, the formula for footcandles (FC) is:
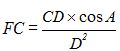
where CD is the candlepower, A is the angle of incidence of the light beam (see diagram under "lux,") and D is the distance of the surface from the light source.
Frangible
The property of a material designed to be readily or easily
broken.
High Mast Illumination Details (HMID)
TxDOT's standard sheets showing specifications for high mast
illumination rings, lowering devices, and related mechanical and
electrical systems.
High Mast Illumination Pole Foundations (HMIF)
TxDOT standard sheets showing specifications for high mast
illumination foundations and drill shafts.
High Mast Illumination Poles (HMIP)
TxDOT standard sheets showing specifications for high mast
illumination poles.
Illuminating Engineering Society of North America (IESNA, also IES)
A non-profit society of lighting engineers and professionals.
The IESNA writes many of the industry standard specifications for
lighting fixtures.
High Mast Lighting
Lighting units mounted at heights of 100 feet or more.
Inductance (L)
Ability to store energy in electromagnetic field. Measured
in henrys or millihenrys.
Kilowatt (KW)
A measure of real power (generators, lamps, and heating elements are rated in watts or kilowatts).
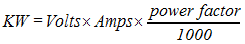
(1KW = 1.34 horse power)
Kilovolt-amp (KVA)
A measure of apparent power. Equipment is rated in KVA when heat dissipation is a concern (transformers are rated in KVA)
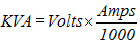
Lamp
A replaceable light source in a glass enclosure. A lamp may
be high pressure sodium, metal halide, fluorescent, incandescent,
or induction fluorescent. Also called a "light bulb."
Light Source
The device that converts electric energy to visible light.
Lumen (lm)
The unit of luminous flux.
Luminaire
A device that directs, controls, and modifies the light produced
by a light source. It consists of a light source, reflector, refractor,
housing, and such support as may be integral with the housing
Lux (lx)
Metric unit of measurement for the illumination (E) on a surface. (See footcandle for English unit.) One lux is the illumination on a surface one meter from and perpendicular to a uniform point source of one candela. The formula for lux is:
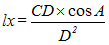
where CD is the candlepower, A is the angle of incidence of the light beam, and D is the distance of the surface from the light source.
Mast Arm
An attachment to a light pole on the end of which a luminaire
is mounted.
Mounting Height
The vertical distance between the base of the pole and the
luminaire.
National Electric Safety Code (NESC)
A standard for the safe installation, operation, and maintenance
of electric supply and communication lines and equipment, for use
by electric utilities.
National Electrical Manufacturer's Association (NEMA)
An organization of electrical manufacturers that develops
specifications and industry standards.
National Fire Protection Association (NFPA)
An organization devoted to eliminating death, injury, property,
and economic loss due to fire, electrical, and related hazards.
The NFPA develops and maintains safety standards such as NFPA 70: National
Electrical Code, and NFPA 70E: Standard for Electrical Safety in
the Workplace.
NFPA 70: National Electric Code (NEC)
An NFPA standard for the safe installation of electrical wiring
and equipment in the United States. The NEC is considered the minimum
acceptable standard for a safe installation. Its purpose is the practical
safeguarding of persons and property from hazards arising from the
use of electricity. An electrical installation that complies with
the NEC will be essentially free from electrical hazard.
NFPA 70E: Standard for Electrical Safety in the Workplace
An NFPA standard for safe work practices to protect personnel
by reducing exposure to major electrical hazards such as electrical
shock, electrocution, arc flash, and arc blast.
Ohm (O)
The unit of electrical resistance.
Partial Interchange Lighting
The lighting of acceleration and deceleration lanes, ramp
terminals, crossroads at frontage road or ramp intersections, and
other areas of nighttime hazard. (See "complete interchange lighting.")
Pole
A galvanized steel or aluminum shaft to support the lighting
unit (also called "lighting standard").
Power (P)
Measured in watts. Formula as follows:
- for DC circuits:P = IE
- for AC circuits:P = IE(pf).
For power loss due to resistance in lighting circuits, the power factor can be considered equal to one. This power can also be calculated: 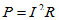 .
.
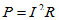 .
.Power Factor (pf)
Time relationship between current wave and voltage wave in
an A.C. system.
PVC
Polyvinyl chloride, a material used for underground non-metallic
conduit.
Reflector
Polished aluminum device used to reflect light.
Refractor
Prismatic glass element used to refract light.
Regulated Output Ballast
A form of electrical transformer that maintains the wattage
of the lamp at a nearly constant value, though the line voltage
may fluctuate as much as ±10 percent. Such ballasts or transformers
may be integrally mounted within the luminaire or separately mounted
in a ballast enclosure.
RMC
Rigid metal conduit.
Roadway Illumination Assembly
The luminaire and supporting members (pole, mast arm, etc.)
with other related lighting equipment attached.
Roadway Illumination Details (RID)
TxDOT's standard sheets showing specifications for roadway
illumination to be used with TxDOT standard specification Item 610.
Roadway Illumination Poles (RIP)
TxDOT standard sheets showing specifications for roadway illumination
poles to be used with TxDOT standard specification Item 610.
Safety Lighting
Roadway lighting installed at interchanges, highway intersections,
and other points of nighttime hazard to the extent necessary to
provide for the safe and orderly movement of traffic.
Starter or Starting Aid (also called igniter)
A device producing a high voltage pulse to begin arcing in
a lamp.
Transformer
An electrical device that changes one AC voltage to another.
Transformer Base
A breakaway device for light poles, also called a T-base.
It is a hollow cast aluminum base, the bottom of which is bolted
to a concrete foundation and to the top of which the bottom flange
of the pole is bolted.
Uniformity
The ratio of the average level of illuminance to the minimum
level of illuminance on the roadway.
Volt (V or E)
The unit of electromotive force, electrical pressure, or difference
of potential. Analogous to water pressure. One volt will cause one
ampere of current to flow through a resistance of one ohm.
Voltage Drop
A result of current flowing through a resistance.
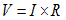
Example:
A current of 30 amperes flowing through 300 feet of No.8 conductor whose resistance loop is 0.3924 ohms will result in a voltage drop of 11.77 volts.Warrant
Warrants are applied to determine whether or not the lighting
system is justifiable at a particular location on an eligible highway.