Section 3: Obtaining Seeds
Introduction
There are several different ways to obtain grass and wildflower
seeds. Typically, seeds are grown by a nursery, harvested and marketed
for commercial sale. This section discusses several sources and
methods of obtaining native plant and wildflower seed.
Nursery Grown Seed
Nursery grown native plant seed are available through commercial sources. Select seed from species adapted to the local growing season, soils and moisture conditions. Select seed that originate within 150-200 miles of the area to be planted, so that they are adapted to local conditions. The TxDOT publication,
“Standard Specifications for Construction and Maintenance of Highways, Streets and Bridges,” Item number
164, contains grass seed recommendations for all districts.Seed must be of the previous season’s crop, with date of analysis shown on each bag. The date must be within 12 months of the time of use.
All grass and wildflower seed must meet the requirements of the Texas Seed Law [Agricultural Code; Title 5, Production, Processing and Sale of Horticultural Products; Subtitle A, Seed and Fertilizer; Chapter 61, Inspection, Labeling and Sale of Agricultural and Vegetable Seed (1981)], including the labeling requirements for showing pure live seed (PLS), name and type of seed. See Section 5, of this Chapter for a full explanation of Pure Live Seed.
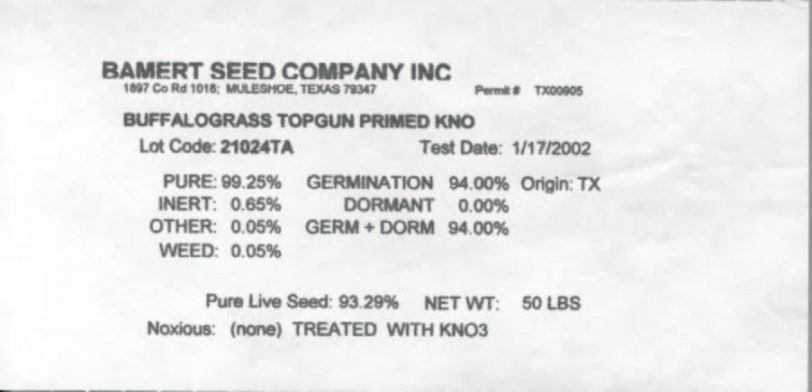
Figure 3-1. Texas Seed Law required Buffalograss seed tag. Courtesy Bamert Seed Co.

Figure 3-2. The certified seed tag indicates that the seed in the corresponding lot has been tested by a Texas Department of Agriculture seed tab. Courtesy Bamert Seed Co.
Stockpiling Topsoil from Roadway Construction Sites
When roadway maintenance and construction activities require
the movement of earth, one of the first steps is to remove and stockpile
a layer of topsoil. This topsoil contains wildflower, native and introduced
grass seeds with viable sprigs of grasses and vegetation from previous
seasons. When the construction or maintenance work nears completion,
the stockpiled topsoil is then replaced over the right of way to
provide native plant, grass and wildflower establishment. Since
this method is not a guarantee for vegetation establishment the
project area should be seeded with the appropriate seed mix for
the district by using,
“Standard Specifications for Construction
and Maintenance of Highways, Streets and Bridges”, Item number
164.
This is the most feasible method used today for a low cost replacement
of topsoil and native vegetation for the right of way.Removal of topsoil from ecologically sensitive areas
or endangered species sites may not be permissible.
The Outdated use of making “Flower Hay”
In years past, seed were gathered from prominent areas of
the right of way where native plants and wildflowers were established
by cutting the area with a sickle mower. This practice was conducted after
the peak blooming period, but before seeds had dropped. The mowed
“flower hay” was then transported to the desired location and simply
scattered over the ground. This method was once used to spread wildflowers
at a cheap cost. Presently, this practice is not a feasible method
because of labor costs and hours involved.