Cutback Asphalt
Cutback asphalt is asphalt cement in which a solvent has been added. The addition of solvent will:
- allow seal coat work during cooler weather when an asphalt cement would cool and set too quickly
- make the binder used in the cutback more fluid
- allow application at lower binder temperatures.
The solvent functions as a carrier or application facilitator. After the application, the solvent evaporates leaving the asphalt cement. In this respect, the use of cutback asphalt is a poor use of solvents that could be used as fuels and these solvents may contribute to air pollution. For these reasons, TxDOT has continued to reduce the amount of cutback asphalt used in construction and maintenance operations.
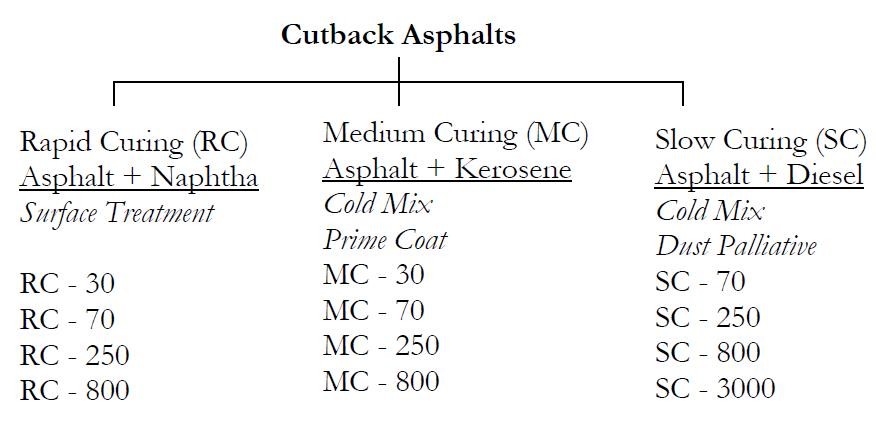
There are two general types of cutback asphalt used by TxDOT: rapid curing (RC) and medium curing (MC). Rapid curing cutbacks contain a solvent in the gasoline-naphtha boiling range. Medium curing cutbacks contain a solvent in the kerosene boiling range. Since gasoline-naphtha is more volatile than kerosene, the solvent in rapid curing cutbacks evaporates faster than the solvent in medium curing cutbacks.
Heating asphalt binder always constitutes some degree of hazard. The most hazardous are cutback asphalts because of the highly volatile solvents used. Extreme care must be taken not to allow any spark or open flame to come in contact with the cutback asphalt or the gases from cutback asphalt due to the low flash point.
As in asphalt cements, rapid and medium curing cutbacks have a nomenclature that describes their solvent and viscosity. A cutback is designated as either RC (rapid curing) or MC (medium curing) to describe the solvent and a number from 30 to 3000 to describe the viscosity. The lower the number, the more solvent is contained in the product. MC-30 contains approximately 35 to 40 percent solvent while an MC-3000 contains only about 5 percent solvent.
RC cutbacks are primarily used for surface treatments on base courses and tack coats. MC cutbacks are primarily used for prime coats and surface treatments on base courses. The specification requirements for cutback asphalt focus on determining the type and amount of solvent used and the stiffness of the asphalt cement in the cutback.
Viscosity.
The viscosity of the cutback is determined to ensure that the viscosity is in the range required by the specification. Viscosity of the cutback is critical to successful application. For instance, MC-30 is used for priming road base. The viscosity must be low enough that the cutback will penetrate (soak into) the base material. It must form a waterproof layer and enable successive asphalt layers to adhere to the base. Each grade of both MCs and RCs has its own viscosity limits.Flash Point.
Flash point is a safety related test. The procedure is similar to that of the asphalt cement. The container geometry is slightly different, but the result is the same. It provides an idea of the temperature at which one can expect the material to generate fumes that could ignite.Distillation.
The distillation test is performed for two reasons: - to examine the characteristics of the cutter stock used in the cutback manufacture
- to examine the characteristics of the residue.
In the test, a sample of cutback asphalt is heated to 680°F. The initial boiling point and the amount of solvent collected at specified temperatures are measured. At 680°F, the remaining asphalt is removed from the heat source and poured into a can for further testing.
Specific Gravity.
Specific gravity is not a specification requirement but is measured to allow for temperature-volume corrections in the field.Penetration/Ductility.
These tests are performed on the residue obtained from distillation. They are indicators of the stiffness and cohesiveness of the asphalt residue. They are performed using the same procedures described in the
section.The following apply to the use of asphalt cement for seal coats:�
- Recommended for use with pre-coated aggregate.�
- TXDOT specified product application temperatures 300° F to 375° F. Recommended 350° F to 375° F.�
- Designed for very quick application and return to traffic. Product “thickens” and creates a “bond” with aggregate quickly as it cools.
- Hot Applied products are designed for efficient quick applications and leave very little room for mistakes.��