4.3 Perpetual Pavement
Perpetual pavement is a term used to describe a long-life structural design. It uses premium HMA mixtures, appropriate construction techniques, and occasional maintenance to renew the surface. Close attention must be paid to proper construction techniques to avoid problems with permeability, trapping moisture, segregation with depth, and variability of density with depth. A perpetual pavement can last 30 years or more if properly constructed and maintained.
In conventional flexible pavements, structural deterioration typically occurs due to either classical bottom-up fatigue cracking, rutting of the HMA layers, or rutting of the subgrade. Perpetual pavement is designed to withstand an almost infinite number of axle loads without structural deterioration by limiting the level of load-induced strain at the bottom of the HMA layers and top of the subgrade and by using deformation-resistant HMA mixtures. Figure 2-3 shows a generalized perpetual pavement design.
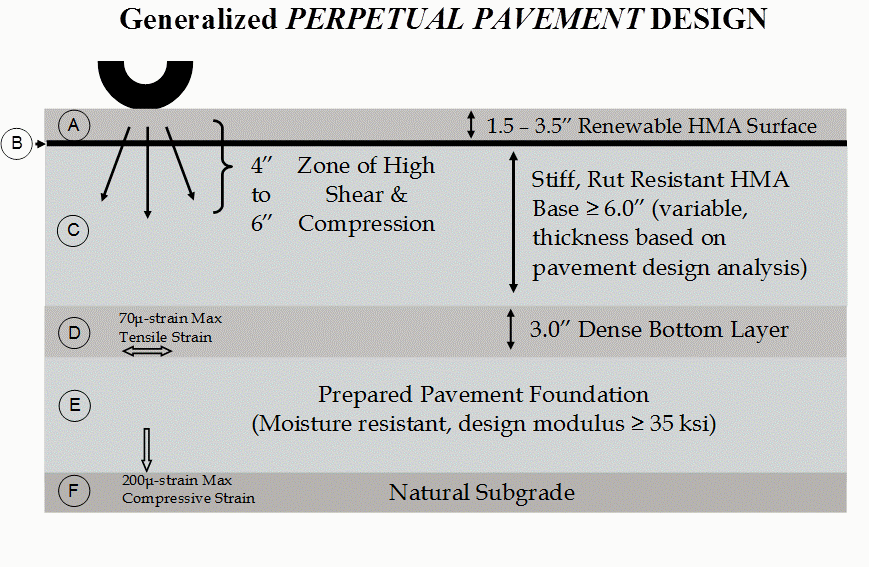
Figure 2-3. Generalized perpetual pavement design.