9.1.2.1 Freeways
A freeway has two or more lanes in each direction access-controlled via ramps. Freeway facilities are typically broken up by “sections” or “segments.” Sections of a freeway are defined as the areas between two ramp gore points. The HCM defines several segment types, including basic, weaving, merge, and diverge segments. See for an illustration of a merge, diverge, and weaving segment. Freeway facilities are typically composed of more segments than sections. Analyzing freeway facilities by sections, by segments, and in its entirety are covered in this chapter.
Segment Type | Sketch-level or macroscopic | HCM-based (mesoscopic) | Microsimulation (microscopic) |
|---|---|---|---|
Freeways (Basic)1 | Travel Demand Model output, Service volume tables | HCS, Freeval, HCM-CALC | Vissim, CORSIM |
Multi-lane Highways (Basic)2 | Travel Demand Model output, Service volume tables | HCS, Freeval, HCM-CALC | Vissim, CORSIM |
Weaving3 | Travel Demand Model output | HCS, Freeval, HCM-CALC | Vissim, CORSIM |
Merge and Diverge4 | Travel Demand Model output | HCM method, HCS, Freeval, HCM-CALC | Vissim, CORSIM |
Two-lane Highways | Travel Demand Model output, Service volume tables | HCS, Freeval, HCM-CALC | Vissim, CORSIM |
Arterial Facilities | Travel Demand Model output, Service volume tables | Synchro, HCS, Freeval, HCM-CALC | Vissim |
Frontage Roads | Synchro or other HCMbased tool | TTI Procedures5 | Vissim |
1
A segment of freeway outside the influence area of any merge (1,500 feet), diverge (1,500 feet), weaving segments (500 feet), or any signalized intersections (2 miles). 2
A segment of highway outside the influence area of any merge (1,500 feet), diverge (1,500 feet), weaving segments (500 feet), or any signalized intersections (2 miles). 3
The crossing of two or more traffic streams traveling in the same direction along a significant length of highway without the aid of traffic control devices. Often formed when merge segments are followed by diverge segments. 4
Primarily occurs at on-ramp and off-ramp junctions with a freeway mainlane. 5
TTI procedures are deterministic but are not HCM-based (mesoscopic). These procedures are discussed in section 3 of this chapter.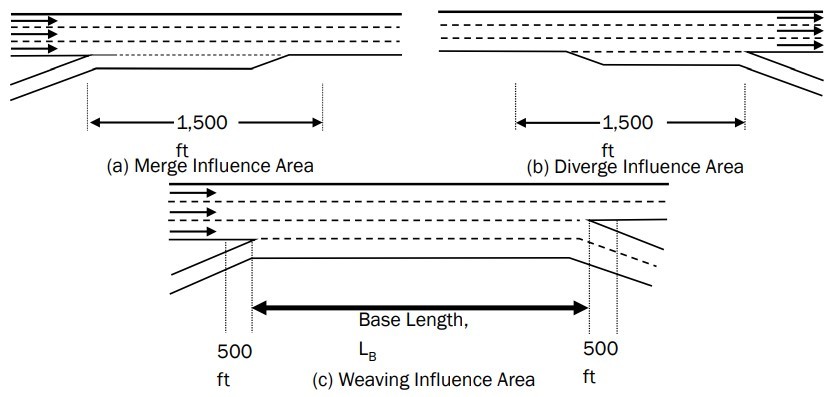
Figure 9-1: Illustration of Merge, Diverge, and Weaving Segments from the HCS7 User Guide (Segment Length subsection)