5.3.3 HSM Part B – Roadway Safety Management Process
Part B of the HSM presents procedures and information that is useful in monitoring and reducing crash frequency and severity on existing roadway networks. This includes the following six steps of the Roadway Safety Management Process:
- Network Screening – Reviewing the existing transportation network to identify and rank individual sites based on the potential for reduction in average crash frequency.
- Diagnosis – Evaluating individual sites based on crash data, historic site data, and field conditions to identify crash patterns.
- Select Countermeasures – Selecting possible countermeasures to reduce the average crash frequency at the site based on the identified factors that may contribute to the crashes.
- Economic Appraisal – Identifying individual projects that are cost effective or economically justified by evaluating the benefits and costs of the possible countermeasures.
- Prioritize Projects – Identifying and prioritizing the set of improvement projects that meet the agency’s objectives, including safety, by evaluating the list of economically justified improvements at a specific site or sites.
- Safety Effectiveness Evaluation – Evaluating the effectiveness of a countermeasure or improvement project at one site or multiple sites in reducing average crash frequency or severity.
The Roadway Safety Management Process is an iterative process to improve the overall safety of the existing roadway network by implementing economically justified projects through data-driven processes. The basic outline of the Roadway Safety Management Process is demonstrated in .
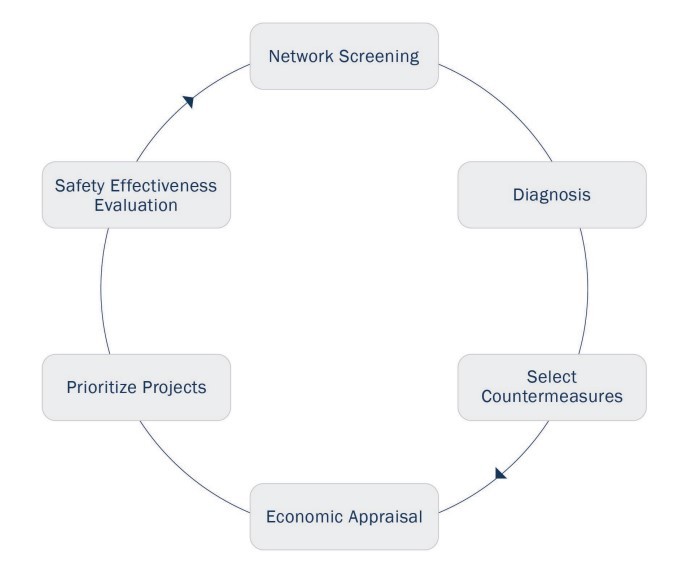
Figure 5-2: Road Safety Management Process