Application of the Kerby-Kirpich Method
An example (shown below) illustrating application of the Kerby-Kirpich method is informative. For example, suppose a hydraulic design is needed to convey runoff from a small watershed with a drainage area of 0.5 square miles. On the basis of field examination and topographic maps, the length of the main channel from the watershed outlet (the design point) to the watershed divide is 5,280 feet. Elevation of the watershed at the outlet is 700 feet. From a topographic map, elevation along the main channel at the watershed divide is estimated to be 750 feet. The analyst assumes that overland flow will have an appreciable contribution to the time of concentration for the watershed. The analyst estimates that the length of overland flow is about 500 feet and that the slope for the overland-flow component is 2 percent (S = 0.02). The area representing overland flow is average grass (N = 0.40). For the overland-flow t
c
, the analyst applies the Kerby equation,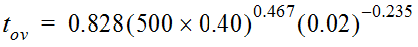
from which t
ov
is about 25 minutes. For the channel tch
, the analyst applies the Kirpich equation, but first dimensionless main-channel slope is required,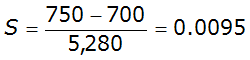
or about 1 percent. The value for slope and the channel length are used in the Kirpich equation,
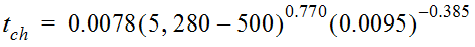
from which t
ch
is about 32 minutes. Because the overland flow tov
is used for this watershed, the subtraction of the overland flow length from the overall main-channel length (watershed divide to outlet) is necessary and reflected in the calculation. Adding the overland flow and channel flow components gives total time of concentration for
a watershed of about 57 minutes. Finally, as a quick check, the analyst can evaluate the tc
by using an ad hoc method representing tc
, in hours, as the square root of drainage area, in square miles. For the example, the square root of the drainage area yields a tc
estimate of about 0.71 hours or about 42 minutes, which is reasonably close to 57 minutes. However, 57 minutes is preferable. This example is shown in Figure 4-7.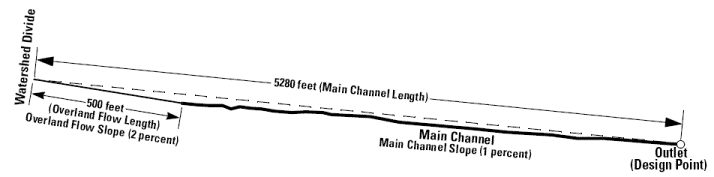
Figure 4-7. Example application of Kerby-Kirpich method