Section 2: Estimated Service Life
Corrugated Metal Pipe and Structural Plate
Determine the service life of corrugated metal structure by calculating the service life of the exterior and interior of the pipe using the site characteristics for the soil and water discussed in the previous section. The overall service life will be the lesser of the interior service life or exterior service life. The service life of a corrugated metal conduit is expressed by the sum of the base metallic coating, post applied coating, and paving or lining service life, as in Equation 14-1 and Equation 14-2:
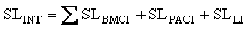
Equation 14-1.
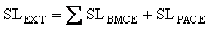
Equation 14-2.
where:
- SLINT= service life of the interior of the pipe
- SLEXT= service life of the exterior of the pipe
- SLBMCI= service life of the base metallic coating interior
- SLBMCE= service life of the base metallic coating exterior
- SLPACI= service life of the post applied coating interior
- SLPACE= service life of the post applied coating exterior
- SLLI= service life of the paving or lining interior
Corrugated Steel Pipe and Steel Structural Plate
The base metallic coating data provided in this section are limited to the following values for galvanized metals:
- 6 < pH < 8
- resistivity ≥ 2,000 ohm-cm
- soft waters considered hostile when resistivity ≥ 7,500 ohm-cm
For aluminized type 2, the following values apply:
- 5.0 < pH < 9.0; Resistivity > 1,500 ohm-cm
- soft waters not considered to be a problem
Estimate the service life for the interior base metallic coating using Equation 14-3
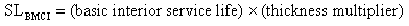
Equation 14-3.
The basic interior service life for 18-gage corrugated galvanized metal pipe is provided in the table following Equation 14-4 for pH values of 7.3 and lower and using the equation for pH values in excess of 7.3.
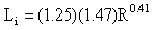
Equation 14-4.
where:
- Li= interior years
- R= resistivity (ohm-mm)
Exterior Coating
Estimate the service life for the basic exterior base metallic coating using Equation14-5.

Equation 14-5.
The basic exterior service life (L
e
) for 18-gage corrugated galvanized metal pipe is provided in the table following Equation 14-6 for pH values of 7.3 and lower and using the equation for pH values in excess of 7.3.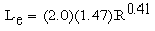
Equation 14-6.
pH | Resistivity (ohm-cm) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1,000 | 1,500 | 2,000 | 2,500 | 3,000 | 4,000 | 5,000 | 7,500 | 10,000 | |
7.3 | 54.8 | 59.6 | 63.1 | 65.8 | 67.9 | 71.4 | 74.1 | 78.9 | 82.4 |
7.0 | 34.6 | 39.4 | 42.9 | 45.6 | 47.7 | 51.2 | 53.9 | 58.7 | 62.2 |
6.5 | 23.9 | 28.8 | 32.2 | 34.9 | 37.1 | 40.5 | 43.2 | 48.0 | 51.5 |
6.0 | 18.0 | 22.9 | 26.3 | 29.0 | 31.2 | 34.6 | 37.3 | 42.1 | 45.6 |
5.8 | 16.2 | 21.0 | 24.5 | 27.2 | 29.3 | 32.8 | 35.5 | 40.3 | 43.8 |
5.5 | 13.8 | 18.6 | 22.1 | 24.8 | 26.9 | 30.4 | 33.1 | 37.9 | 41.4 |
5.0 | 10.4 | 15.3 | 18.7 | 21.4 | 23.6 | 27.0 | 29.7 | 34.5 | 38.0 |
Heavier gage metal has more sacrificial metal and, therefore, a longer anticipated life under given conditions. The table below provides coating thickness/gage multipliers for use in Equation 14-1 and Equation 14-2 for the respective gage and metallic coating. The resulting values are not exact but allow a systematic comparison of relative durability of the various metals and gages used in design.
Gauge | Item 460 - CMP | Item 461 - Structural Plate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Thickness | Factor | Thickness | Factor | ||
in. (mm) | Galv | Alt 2 | in. (mm) | Galv | |
18 | 0.052 (1.32) | 1 | 3.6 | ** | ** |
16 | 0.064 (1.63) | 1.3 | 3.9 | ** | ** |
14 | 0.079 (2.01) | 1.6 | 4.2 | ** | ** |
12 | 0.109 (2.77) | 2.2 | 4.8 | 0.109 (2.77) | 2.24 |
10 | 0.138 (3.50) | 2.8 | 5.4 | 0.138 (3.50) | 2.84 |
8 | 0.168 (4.27) | 3.4 | 6 | 0.168 (4.27) | 3.54 |
7 | ** | ** | ** | 0.188 (4.78) | 3.81 |
5 | ** | ** | ** | 0.218 (5.54) | 4.42 |
3 | ** | ** | ** | 0.249 (6.32) | 5.05 |
1 | ** | ** | ** | 0.280 (7.11) | 5.68 |
Corrugated Aluminum Pipe and Aluminum Structural Plate
The service life of aluminum pipe and aluminum structural plate is a function of the pitting rate of the aluminum, which is less than 0.013 millimeter per year in the following environmental limits:
- 4.0 ≤ pH ≤ 9.0
- resistivity ≥ 500 ohm-cm
- resistivity ≥ 25 ohm-cm (provided a free draining backfill material)
- no upper resistivity limits; soft waters not a problem
Estimate interior service life (SL
BMCI
) and exterior service life (SLBMCE
) using Equation14-7.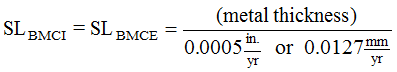
Equation 14-7.
The following table shows gage thickness and available structural plate thickness.
Item 460 – CMP | Item 461 – Structural Plate | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Gage | Thickness | Gage | Thickness | ||
(in) | (mm) | (in) | (mm) | ||
18 | 0.048 | 1.22 | ** | ** | ** |
16 | 0.06 | 1.52 | ** | ** | ** |
14 | 0.075 | 1.91 | ** | ** | ** |
12 | 0.15 | 2.67 | ** | 0.1 | 2.54 |
10 | 0.135 | 3.43 | ** | 0.125 | 3.18 |
8 | 0.164 | 4.17 | ** | 0.15 | 3.81 |
** | ** | ** | ** | 0.175 | 4.45 |
** | ** | ** | ** | 0.2 | 5.08 |
** | ** | ** | ** | 0.225 | 5.72 |
** | ** | ** | ** | 0.25 | 6.35 |
Post-applied Coatings and Pre-coated Coatings
The following table provides anticipated additional service life for post-applied and pre-coated coatings (SL
PACI
and SLPACE
) for use in Equation14-1 and Equation14-2.Coating | Interior (SL PACE ) | Exterior (SL PACE ) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Abrasion Level | |||||
Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Level 4 | ||
Bituminous | 8-10 | 5-8 | 0-2 | 0 | 30 |
Polymer 10/10 | 28-30 | 10-15 | 0-5 | 0 | 30 |
Paving and Lining
The following table provides additional service life for applied paving and lining (SL
l
) for use in Equation14-1.Paved Or Lined | Interior | Exterior | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Abrasion Level (SL LL ) | |||||
Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Level 4 | ||
Bituminous Paved Invert | 25 | 25 | 25 | 0 | N/A |
Concrete Paved Invert | 40 | 40 | 40 | 25 | N/A |
100% Bituminous Lined | 25 | 25 | 25 | 0 | N/A |
100% Concrete Lined | 50 | 50 | 50 | 35 | N/A |
Reinforced Concrete
There is little technical data on methods to estimate service life for reinforced concrete. In department experience when cast-in-place and precast reinforced conduit is used in appropriate environments, service life exceeds the original design life of the project (typically in excess of 50 years).
Durability of reinforced concrete can be affected by acids, chlorides, and sulfate concentrations in the soil and water. If the pH value is 6.5 or less, the use of porous concrete pipe with shell thickness of 1 in. (25 mm) or less is not advisable. If the pH value is 5.5 or less, use of reinforced concrete without a protective coating of epoxy or other acceptable coating is not advisable.
Salt content of the soil and water can have a detrimental effect on reinforced concrete because the salt (with its chloride constituent) can permeate the concrete in time, threatening the embedded reinforcing steel. Sulfate content in the soil or water can have a detrimental effect on reinforced concrete facilities. The following table presents a guide for adjusting cement type and factor for sulfate content in soils and runoff.
Water-soluble sulfate in soil sample (%) | Sulfate in water sample (ppm) | Type of cement | Cement factor |
|---|---|---|---|
0 - 0.20 | 0 - 2,000 | II | Minimum required by specifications |
0.20 - 0.50 | 2,000 - 5,000 | V II | Minimum required by specifications 7 sacks |
0.50 - 1.50 | 5,000 - 15,000 | V II | Minimum required by specifications 7 sacks |
over 1.50 | over 15,000 | V | 7 sacks |
Plastic Pipe
To date, the department has minimal long-term experience with plastic pipe applications. More information will be provided as the department becomes aware of appropriate information. However, this lack of information should not preclude the possible use of plastics that conform to AASHTO and ASTM specifications if there is solid indication that the particular installation will meet service life expectations.