Storage Design Guidelines
The storage volume of the wet well should be less than the total volume of the wet well because allowances should be made for a sump and for freeboard. The sump is the volume of the wet well below the required minimum water level, which is the pump cutoff elevation. The wet well must maintain water above the pump inlet to keep the pump from attempting to pump dry or sucking air. The sump must also have room below the pump intake level for sedimentation and heavy trash that wash into the system.
The top of the storage volume determines the maximum water level, the level in the wet well above which the water should not be allowed to exceed. Any freeboard above the maximum water level is not included in the calculated storage volume. Pumping is initiated at or below the maximum water level, and is stopped when the water drops to the minimum water level.
Other spaces outside of the wet well which can store storm water before flooding occurs may also be considered part of the available storage volume. These include sumps, pipes, boxes, inlets, manholes, and ditches of the storm drain system. The storm drain system can represent a significant storage capacity.
Figures 11-2 and 11-3 are a pump station location plan and cross section. The cross section shows how the storm system can provide additional storage outside of the wet well.
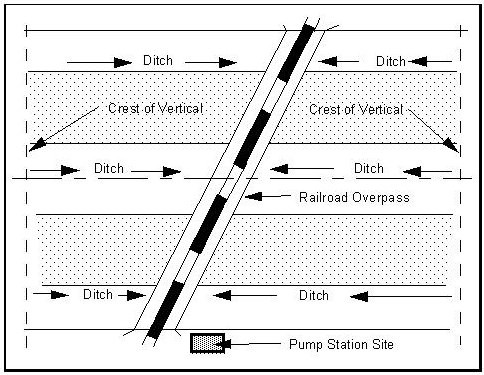
Figure 11-2. Pump Station Schematic
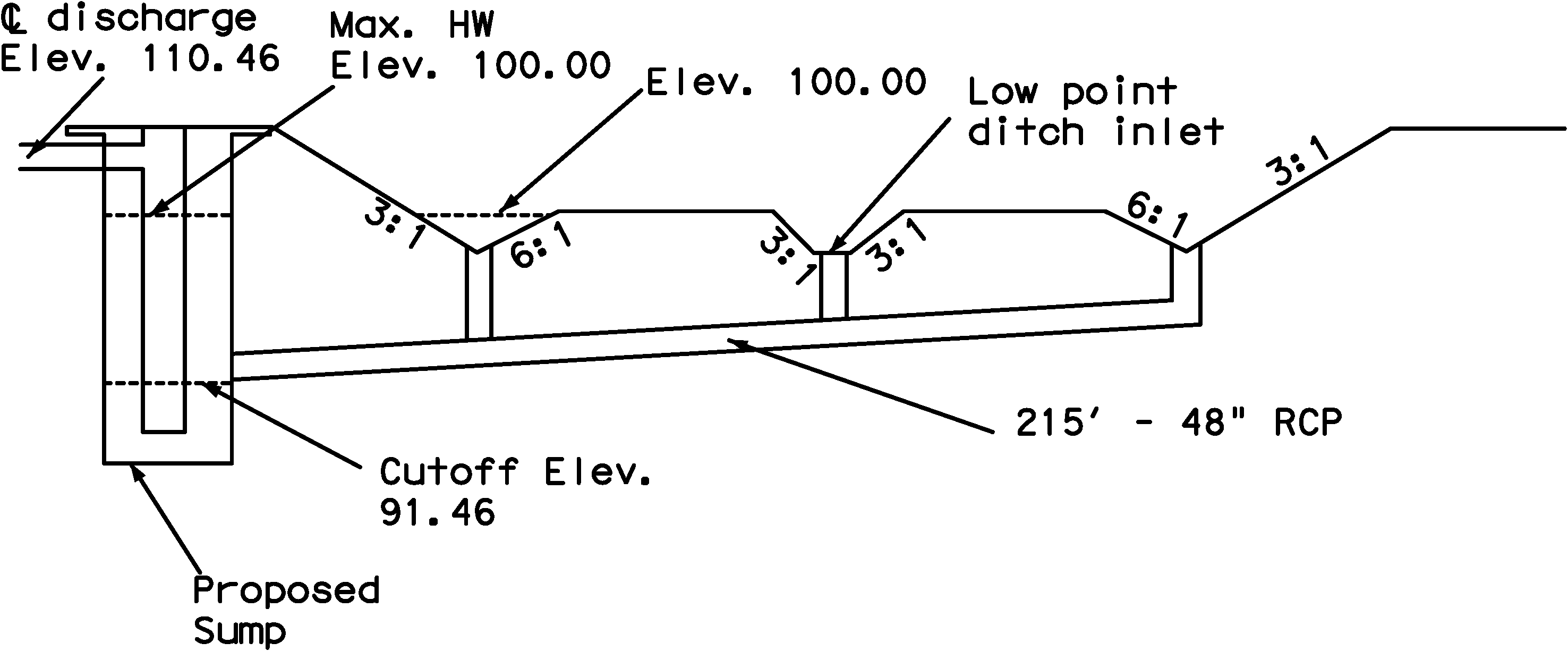
Figure 11-3. Typical Cross Section