Curb Inlets in Sag Configuration
The capacity of a curb inlet in a sag depends on the water depth at the curb opening and the height of the curb opening. The inlet operates as a weir to depths equal to the curb opening height and as an orifice at depths greater than 1.4 times the opening height. At depths between 1.0 and 1.4 times the opening height, flow is in a transition stage and the capacity should be based on the lesser of the computed weir and orifice capacity. Generally, for Department design, this ratio should be less than 1.4 such that the inlet operates as a weir.
- If the depth of flow in the gutter (y) is less than or equal to 1.4 times the inlet opening height (h), ( y ≤ 1.4h ), determine the length of inlet required considering weir control. Otherwise, skip this step. Calculate the capacity of the inlet when operating under weir conditions with Equation 10-14.
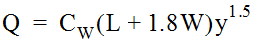 Equation 10-14.Equation 10-14 is rearranged to produce the following relation for curb inlet length required.
Equation 10-14.Equation 10-14 is rearranged to produce the following relation for curb inlet length required.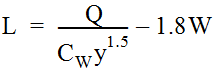 Equation 10-15.where:
Equation 10-15.where:- Q= total flow reaching inlet (cfs or m3/s)
- C= weir coefficient (ft.w0.5/s or m0.5/s)
- Suggested value = 2.3 ft.0.5/s or 1.27 m0.5/s for depressed inlets
- Suggested value = 3.0 ft0.5/s or 1.60 m0.5without depression
- y= head at inlet opening (ft. or m), computed with Equation 10-1
- L= length of curb inlet opening (ft. or m)
- W= gutter depression width (perpendicular to curb)
- If L > 12 ft. (3.6m), then W = 0 and CW= 3.0 ft.0.5/s or 1.60 m0.5/s.
- If the depth of flow in the gutter is greater than the inlet opening height (y > h), determine the length of inlet required considering orifice control. The equation for interception capacity of a curb opening operating as an orifice follows:
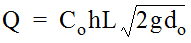 where:Equation 10-16.
where:Equation 10-16.- Q= total flow reaching inlet (cfs or m3/s)
- Co= orifice coefficient = 0.67
- h= depth of opening (ft. or m)(this depth will vary slightly with the inlet detail used)
- L= length of curb opening inlet (ft. or m)
- g= acceleration due to gravity = 32.2 ft./s2or 9.81 m/s2
- d= effective head at the centroid of the orifice (ft. or m).o
For curb inlets with an inclined throat such as Type C inlet, the effective head, do, is at the centroid of the orifice. This changes Equation 10-16 to: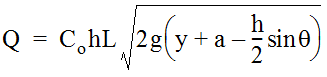 Equation 10-17.where:Q= total flow reaching inlet (cfs or m3/s)C= orifice coefficient = 0.67oh= depth of opening (ft. or m)(this depth will vary slightly with the inlet detail used)L= length of curb opening inlet (ft. or m)g= acceleration due to gravity = 32.2 ft/s2or 9.81 m/s2y= depth of water in the curb and gutter cross section (ft. or m)a= gutter depression depth (ft.). Rearranging Equation 10-17 allows a direct solution for required length.
Equation 10-17.where:Q= total flow reaching inlet (cfs or m3/s)C= orifice coefficient = 0.67oh= depth of opening (ft. or m)(this depth will vary slightly with the inlet detail used)L= length of curb opening inlet (ft. or m)g= acceleration due to gravity = 32.2 ft/s2or 9.81 m/s2y= depth of water in the curb and gutter cross section (ft. or m)a= gutter depression depth (ft.). Rearranging Equation 10-17 allows a direct solution for required length. 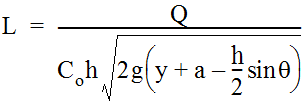 Equation 10-18.
Equation 10-18.- If both steps 1 and 2 were performed (i.e., h < d ≤ 1.4 h ), choose the larger of the two computed lengths as being the required length.
- Select a standard inlet length that is greater than the required length.